How can you manufacture ethanol?
Methods
§1. Catalytic addition of steam on Ethene
§2. Fermentation of Glucose
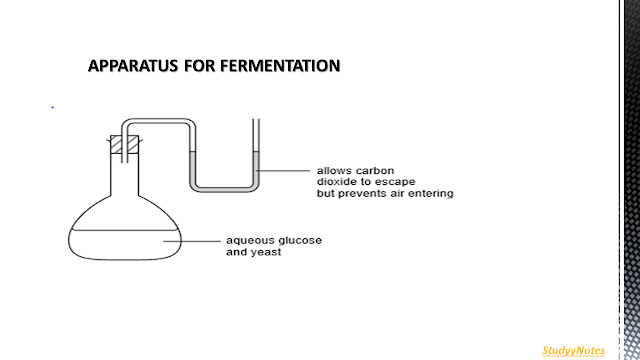
FERMENTATION OF GLUCOSE SOLUTION
§Glucose solution on fermentation gives ethanol & carbon dioxide
§Exothermic reaction
§Word equation
glucose solution à ethanol + carbon dioxide
§Chemical equation:
§
C6H12O6 [aq] à2CH3CH2OH[aq] + 2CO2 [g]
§Catalyst: Enzyme present in yeast
§Temp range : 25 – 40 degree Celsius
§Optimum temp 35 degree Celsius
§Define Respiration?
§Process by which living things break down food to produce energy.
§What are enzymes?
§Enzymes are proteins or biological catalyst.
OBSERVATIONS DURING FERMENTATION
§BUBBLES OF GAS
§SLIGHT INCREASE IN TEMPERATURE
METHOD 1: FERMENTATION
Disadvantage: Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas.
Disadvantage: Growing the crop uses land that could be used for food.
Disadvantage: Batch process.
Advantage: It uses plants and so is a renewable source of ethanol.
METHOD 2: CATALYTIC ADDITION OF STEAM
Disadvantage: Needs high temperatures/pressures.
Disadvantage: Uses a lot of energy.
Disadvantage: Ethene is made from crude oil which will run out.
Advantage: Continuous process.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
§Why is a two way tap used?
..Not to let oxygen/bacteria enter
..To remove carbon dioxide
§Why should carbon dioxide produced be removed?
.. More carbon dioxideà more acidic àenzyme denatures
.. More carbon dioxide à more pressure
§Conditions where enzymes denatures?
.. More carbon dioxideà more acidic àenzyme denatures
.. If concentration of ethanol> 15% àenzyme denatures
.. If temperature above 40 degree Celsius àenzyme denatures
§Why oxygen should not be allowed to enter?
.. To prevent aerobic respiration
.. To prevent oxidation of ethanol to ethanoic acid
§Why is it necessary to add yeast?
.. Yeast is a catalyst, provides enzymes
§Suggest why the amount of yeast in the mixture increases.
.. Yeast cells grow or reproduce
§Why is a higher temperature not used in this reaction?
.. Higher temp kills yeast or denatures enzyme
.. Hence reduces rate of reactions
§Why does fermentation stops?
.. Glucose is used up
.. Enzyme denatured/yeast cells killed








 07:43:00
07:43:00
 StudyyNotes
StudyyNotes











 Posted in:
Posted in: